The system to be solved is :
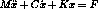 with F defined by
with F defined by 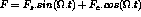
Test name
vibr10
Calculation type
MECHANICS DYNAMICS
MASS UNBALANCE RESPONSE
Finite element type
Topic
Mass unbalance response.
The system is represented by a point (mass M1, stiffness K1). A mass unbalance is added in the equation under the shape of a force.
The system to be solved is : 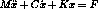 with F defined by
with F defined by 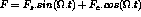
The response is computed with VIBC operator and its option BALOUR.
Goal
Find the small and big axes of the ellipse described by the system.
Reference
Analytical solution.
Version
97' customer version
Model description
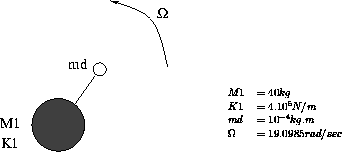
Results
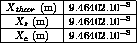
* Test Vibr10.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* ---------------------------------- *
* *
*************************************************
* TEST : VIBR10 *
* *
* Calcul de la reponse au balourd *
* Test de l'option 'BALOU de l'operateur *
* VIBC *
*************************************************
OPTI 'DIME' 3 'ELEM' SEG2 ;
*
*donnees
P1 = 1. 0. 0. ;
m1 = 40. ;
k1 = 4.e5 ;
f1 = ((k1 / m1) ** 0.5) / (2. * pi) ;
MESS 'f1 =' f1 ;
*
TR1 = MANU 'POI1' P1 ;
*
*Matrices de masse et de rigidite :
MMass = MANU 'RIGI' TR1 (MOTS 'UY' 'UZ')
(PROG m1 0. 0. m1) ;
MRigi = MANU 'RIGI' TR1 (MOTS 'UY' 'UZ')
(PROG k1 0. 0. k1) ;
*
*deformees modales :
Phi1 = MANU 'CHPO' TR1 2 'UY' 1. 'UZ' 0. ;
Phi2 = MANU 'CHPO' TR1 2 'UY' 0. 'UZ' 1. ;
*
*points reperes des modes
PR1 = 0. 0. 0. ;
PR2 = 0. 0. 0. ;
*
*base des mods reels :
TBasR = TABLE 'BASE_MODALE' ;
TBasR.MODES = TABLE 'BASE_DE_MODES' ;
TBasR.MODES . 'MAILLAGE' = TR1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 1 = TABLE 'MODE' ;
TBasR.MODES . 1 . 'NUMERO_MODE' = 1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 1 . 'POINT_REPERE' = PR1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 1 . 'FREQUENCE' = f1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 1 . 'MASSE_GENERALISEE' = m1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 1 . 'DEPLACEMENTS_GENERALISES' =
k1 - (2 * pi * f1) ;
TBasR.MODES . 1 . 'DEFORMEE_MODALE' = Phi1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 2 = TABLE 'MODE' ;
TBasR.MODES . 2 . 'NUMERO_MODE' = 2 ;
TBasR.MODES . 2 . 'POINT_REPERE' = PR2 ;
TBasR.MODES . 2 . 'FREQUENCE' = f1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 2 . 'MASSE_GENERALISEE' = m1 ;
TBasR.MODES . 2 . 'DEPLACEMENTS_GENERALISES' =
k1 - (2 * pi * f1) ;
TBasR.MODES . 2 . 'DEFORMEE_MODALE' = Phi2 ;
*
*vitesse (rad/s)
omeg1 = 19.0985 ;
*
*-projection des matrices sur la base réelle :
MMasP = PJBA TBasR MMass ;
MRigP = PJBA TBasR MRigi ;
*
*-calcul de la force d'excitation du balourd
MxD = 1e-4 ;
Fy1s = MxD * (omeg1 ** 2) ;
Fz1s = (-1) * MxD * (omeg1 ** 2) ;
Fy1c = MxD * (omeg1 ** 2) ;
Fz1c = MxD * (omeg1 ** 2) ;
*
F1s = MANU 'CHPO' P1 2 'FY' Fy1s 'FZ' Fz1s ;
F1c = MANU 'CHPO' P1 2 'FY' Fy1c 'FZ' Fz1c ;
PjF1s = PJBA F1s TBasR ;
PjF1c = PJBA F1c TBasR ;
*
GEOx1 = EXTR PjF1s 'MAIL' ;
GEOx2 = GEOx1 ;
*
XVal1 = PROG ;
XVal2 = PROG ;
REPE bbb2 (NBEL GEOx1) ;
i2 = &bbb2 ;
XP1 = 0. 0. 0. ;
GEOx2 = GEOx2 ET XP1 ;
Px1 = POIN GEOx1 i2 ;
XVal1 = XVal1 ET (PROG (EXTR PjF1s 'FALF' Px1)) ;
XVal2 = XVal2 ET (PROG (EXTR PjF1c 'FALF' Px1)) ;
FIN bbb2 ;
XVal2 = XVal1 ET XVal2 ;
*
PjFBal1 = MANU CHPO GEOx2 1 'FALF' XVal2 ;
*
*-calcul de la reponse :
RepRe1 RepIm1 = VIBC 'BALOU' MMasP MRigP TBasR
PjFBal1 omeg1 ;
*
*-calcul des pt et gd axes de l'ellipse :
YR1 = EXTR RepRe1 'UY' P1 ;
ZR1 = EXTR RepRe1 'UZ' P1 ;
MESS YR1 ZR1 ;
*
*-resultats attendus :
An1= (MxD * (omeg1 ** 2)) / (k1 - ((omeg1 ** 2) * m1));
MESS 'resultats attendus : ' An1 ;
*
FIN ;
Test vibr10 Comments
F1s = MANU 'CHPO' P1 2 'FY' Fy1s 'FZ' Fz1s ;
F1c = MANU 'CHPO' P1 2 'FY' Fy1c 'FZ' Fz1c ;
PjF1s = PJBA F1s TBasR ;
PjF1c = PJBA F1c TBasR ;
GEOx1 = EXTR PjF1s 'MAIL' ;
GEOx2 = GEOx1 ;
**
XVal1 = PROG ;
XVal2 = PROG ;
REPE bbb2 (NBEL GEOx1) ;
i2 = &bbb2 ;
XP1 = 0. 0. 0. ;
GEOx2 = GEOx2 ET XP1 ;
Px1 = POIN GEOx1 i2 ;
XVal1 = XVal1 ET (PROG (EXTR PjF1s 'FALF' Px1)) ;
XVal2 = XVal2 ET (PROG (EXTR PjF1c 'FALF' Px1)) ;
FIN bbb2 ;
XVal2 = XVal1 ET XVal2 ;
**
PjFBal1 = MANU CHPO GEOx2 1 'FALF' XVal2 ;
The mass unbalance force ( PjFBal1) is expressed relatively to a real eigen mode basis. It is a CHAMPOIN object with one dual component FALF.
It must be obtained by the following way :
- Both components 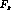 and
and 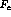 are separated into two CHAMPOIN objects (here F1s and F1c).
are separated into two CHAMPOIN objects (here F1s and F1c).
- Those two CHAMPOIN objects are projected on the n real eigen mode basis (here TBasR basis is composed of 2 eigen modes). The projected objects are PjF1s and PjF1c.
- Then PjF1s and PjF1c are combined in order to obtain a 2 x n vector that is to say a CHAMPOIN object composed by one component FALF and supported by 4 points (GEOx2)
RepRe1 RepIm1 = VIBC 'BALOU' MMasP MRigP TBasR PjFBal1 omeg1 ;
The operator VIBC followed by BALOU keyword computes the complex solutions in the case of an unbalanced excitation. It creates two CHAMPOIN objects (RepRe1 and RepIm1) which contain the displacement vectors :
- RepRe1 deals with 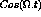 components, and the real components.
components, and the real components.
- RepIm1 deals with 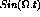 components, and the imaginary components.
components, and the imaginary components.