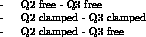
Test name
dyna5
Calculation type
MECHANICS DYNAMICS 3D
SUB-STRUCTURATION
Finite element type
POUT
Topic
Methods of sub-structuration.
The problem consists in using sub-structuration methods to find
the natural frequency of a clamped-clamped beam. The beam is
decomposed in two pieces of same length.
The three methods correspond to the three different ways to describe the constraints between the two common tips Q2 and Q3 :
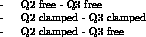
Goal
Find the first natural frequency of the beam.
Reference
Analytical solution.
Version
97' customer version
Model description
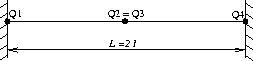

Test dyna5 Results
Results

CASTEM figures
* Test Dyna5.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* --------------------------------- *
* *
* CAS TEST DU 92/01/07 PROVENANCE : PHIL
OPTI ECHO 0;
GRAPH='N';
SAUT PAGE ;
*******************************************************
*
* DYNA5 - Test de sous-structuration par 3 méthodes
*
* La fréquence propre d'une poutre est égale à 65 Hz.
* On se propose de retrouver cette fréquence par trois
* méthodes de sous-structuration.
*
* Pour cela on décompose la poutre en deux morceaux
* de meme longueur.
*
*
* Q1 poutre 1 Q2
* .--------------..------------.
* Q3 poutre 2 Q4
*
*
* Les trois méthodes de sous-structuration correspon-
* dent aux conditions aux limites de l'extrémité
* commune Q2 et Q3 des deux morceaux de poutres :
* * Q2 libre - Q3 libre
* * Q2 bloqu{ - Q3 bloqué
* * Q2 bloqu{ - Q3 libre
*
* A ces trois méthodes correspondent trois manières de
* décrire les liaisons entre sous-structures
* (opérateur RELA).
*
*******************************************************
*
TITRE 'DYNA5 - METHODES DE SOUS-STRUCTURATION' ;
OPTIO DIME 3 ELEM SEG2 MODE TRID IMPI 0;
OPTION TRAC BENS;
SOL=TABLE;
TEMPS ;
*
*______________________________________________________
* PREMIERE METHODE LIBRE-LIBRE
*______________________________________________________
*
*---- Définition de la géométrie de la 1ère poutre ----
*
Q1 = 0. 0. 0.; Q2 =2. 0. 0.;
LIG1= D 12 Q1 Q2;
OEIL1 = 5 5 5 ;
* TRACE OEIL1 LIG1 ;
*
*---- Type de calcul, matériau et caractéristiques ----
*---------------- de la 1ère poutre -------------------
*
MO1= MODL LIG1 MECANIQUE ELASTIQUE POUT ;
MATPL1=MATR MO1 YOUNG 2.E11 NU 0.3 RHO 7800;
CARPL1=CARB MO1 SECT 0.1 INRY 2.08E-7 INRZ 3.33E-8
TORS 2.41E-7;
MATPL1=MATPL1 ET CARPL1;
*
*------ Rigidité, masse et conditions aux limites -----
*----------------- de la 1ère poutre ------------------
*
RIGPL1 =RIGI MATPL1 MO1 ;
MASPLA1=MASS MATPL1 MO1 ;
BLOQ1=BLOQ DEPL ROTA Q1 ;
RIGPLA1=RIGPL1 ET BLOQ1 ;
*
*---- Recherche des modes propres de la 1ère poutre ---
*
PR=PROG 0.4 ;
MODPLA1=VIBR PROC PR RIGPLA1 MASPLA1;
*
*---- Définition de la géométrie de la 2ème poutre ----
*
Q3 =2. 0. 0.; Q4 =4. 0. 0.;
LIG2= D 12 Q3 Q4;
* TRAC OEIL1 LIG2 ;
*
POUTRE=LIG1 ET LIG2 ;
SI(NEG GRAPH 'N');
TRAC OEIL1 POUTRE;
FINSI;
*
*---- Type de calcul, matériau et caractéristiques ----
*---------------- de la 2ème poutre -------------------
*
MO2= MODL LIG2 MECANIQUE ELASTIQUE POUT ;
MATPL2=MATR MO2 YOUNG 2.E11 NU 0.3 RHO 7800;
CARPL2=CARB MO2 SECT 0.1 INRY 2.08E-7 INRZ 3.33E-8
TORS 2.41E-7;
MATPL2=MATPL2 ET CARPL2;
*
*----- Rigidité, masse et conditions aux limites ------
*---------------- de la 2ème poutre -------------------
*
RIGPL2 =RIGI MATPL2 MO2 ;
MASPLA2=MASS MATPL2 MO2 ;
BLOQ4=BLOQ DEPL ROTA Q4;
RIGPLA2=RIGPL2 ET BLOQ4 ;
*
*---- Recherche des modes propres de la 2ème poutre ---
*
MODPLA2=VIBR PROC PR RIGPLA2 MASPLA2;
*
* Création des sous-structures associées aux 2 poutres
*
SPLA1=STRU RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
SPLA2=STRU RIGPLA2 MASPLA2 ;
ELM2=ELST Q2 SPLA1;
ELM3=ELST Q3 SPLA2;
PR2=PROG 1. ;PR3=PROG -1. ;
*
*--- Description des liaisons entre sous-structures ---
*
LIUX=RELA ELM2 UX PR2 ELM3 UX PR3;
LIUY=RELA ELM2 UY PR2 ELM3 UY PR3;
LIUZ=RELA ELM2 UZ PR2 ELM3 UZ PR3;
LIRX=RELA ELM2 RX PR2 ELM3 RX PR3;
LIRY=RELA ELM2 RY PR2 ELM3 RY PR3;
LIRZ=RELA ELM2 RZ PR2 ELM3 RZ PR3;
ENCL=LIUY ET LIRX ET LIRY ET LIRZ ET LIUX ET LIUZ;
*
* -Création des bases modales associées aux 2 poutres -
*
BASE1=BASE SPLA1 MODPLA1 ENCL ;
BASE2=BASE SPLA2 MODPLA2 ENCL ;
*
*------------------ Base modale totale ----------------
*---------------- correspondant à la réunion des ------
*------------------- deux bases élémentaires ----------
*
BASET= BASE1 ET BASE2 ;
RIGMO = RIGI BASET ;
MASMO = MASS BASET ;
*
*------------ Recherche de la 1ère fréquence ----------
*------------ propre de la structure totale -----------
*
SOL.1= VIBR PROC (PROG 0.65) MASMO RIGMO ;
FREQ1=TIRE SOL.1 FREQ RANG 1;
*
*
*______________________________________________________
* DEUXIEME METHODE BLOQUE-BLOQUE
*______________________________________________________
*
*
*-------------------- Conditions aux limites ----------
*--------------- sur l'extrémité de la 1ère poutre ----
*
BLOQUX2=BLOQ UX Q2;
BLOQUY2=BLOQ UY Q2;
BLOQUZ2=BLOQ UZ Q2;
BLOQRX2=BLOQ RX Q2;
BLOQRY2=BLOQ RY Q2;
BLOQRZ2=BLOQ RZ Q2;
*
*------------ Rigidité de la 1ère poutre --------------
*
RIGPLA1=RIGPL1 ET BLOQ1
ET BLOQUX2 ET BLOQUY2 ET BLOQUZ2 ET BLOQRX2 ET
BLOQRY2 ET BLOQRZ2;
*
*---- Recherche des modes propres de la 1ère poutre ---
*
PR1=PROG 2.6 ;
MODPLA1=VIBR PROC PR1 RIGPLA1 MASPLA1;
*
*---------------- Conditions aux limites --------------
*------------ sur l'extrémité de la 2ème poutre -------
*
*- Le point Q2 de la 1ère poutre et le point Q3 de la -
*-------- 2ème poutre ont les memes coordonnées -------
*
BLOQUX3=BLOQ UX Q3;
BLOQUY3=BLOQ UY Q3;
BLOQUZ3=BLOQ UZ Q3;
BLOQRX3=BLOQ RX Q3;
BLOQRY3=BLOQ RY Q3;
BLOQRZ3=BLOQ RZ Q3;
*
*------------ Rigidité de la 2ème poutre --------------
*
RIGPLA2=RIGPL2 ET BLOQ4
ET BLOQUX3 ET BLOQUY3 ET BLOQUZ3 ET BLOQRX3 ET
BLOQRY3 ET BLOQRZ3;
*
*---- Recherche des modes propres de la 2ème poutre ---
*
MODPLA2=VIBR PROC PR1 RIGPLA2 MASPLA2;
*
* Création des sous structures associées aux 2 poutres
*
SPLA1=STRU RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
SPLA2=STRU RIGPLA2 MASPLA2 ;
CLUX2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQUX2;
CLUY2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQUY2;
CLUZ2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQUZ2;
CLRX2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQRX2;
CLRY2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQRY2;
CLRZ2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQRZ2;
CLUX3=CLST SPLA2 BLOQUX3;
CLUY3=CLST SPLA2 BLOQUY3;
CLUZ3=CLST SPLA2 BLOQUZ3;
CLRX3=CLST SPLA2 BLOQRX3;
CLRY3=CLST SPLA2 BLOQRY3;
CLRZ3=CLST SPLA2 BLOQRZ3;
*
*--- Description des liaisons entre sous-structures ---
*
PR2=PROG 1. 1.;PR3=PROG 1. 1.;
LIUX=RELA CLUX2 LX PR2 CLUX3 LX PR3;
LIUY=RELA CLUY2 LX PR2 CLUY3 LX PR3;
LIUZ=RELA CLUZ2 LX PR2 CLUZ3 LX PR3;
LIRX=RELA CLRX2 LX PR2 CLRX3 LX PR3;
LIRY=RELA CLRY2 LX PR2 CLRY3 LX PR3;
LIRZ=RELA CLRZ2 LX PR2 CLRZ3 LX PR3;
ENCL=LIUY ET LIRX ET LIRY ET LIRZ ET LIUX ET LIUZ;
*
*--------- Création des bases modales élémentaires ----
*------------- associées aux deux poutres -------------
*
BASE1=BASE SPLA1 MODPLA1 ENCL ;
BASE2=BASE SPLA2 MODPLA2 ENCL ;
*
*------------------ Base modale totale ----------------
*------------- correspondant à la réunion des ---------
*---------------- deux bases élémentaires -------------
*
BASET= BASE1 ET BASE2 ;
RIGMO = RIGI BASET ;
MASMO = MASS BASET ;
*
*------------- Recherche de la 1ère fréquence ---------
*-------------- propre de la structure totale ---------
*
SOL.2= VIBR PROC (PROG 0.65) MASMO RIGMO ;
FREQ2=TIRE SOL.2 FREQ RANG 1;
*
*
*______________________________________________________
* TROISIEME METHODE LIBRE-BLOQUE
*______________________________________________________
*
*
*------------ Rigidité et conditions aux limites ------
*----------------- de la 1ère poutre ------------------
*
RIGPLA1=RIGPL1 ET BLOQ1
ET BLOQUX2 ET BLOQUY2 ET BLOQUZ2 ET BLOQRX2 ET BLOQRY2
ET BLOQRZ2;
*
*---- Recherche des modes propres de la 1ère poutre ---
*
PR1=PROG 2.6;
MODPLA1=VIBR PROC PR1 RIGPLA1 MASPLA1;
*
*-------- Rigidité et conditions aux limites ----------
*--------------- de la 2ème poutre --------------------
*
RIGPLA2=RIGPL2 ET BLOQ4;
*
*---- Recherche des modes propres de la 2ème poutre ---
*
PR2=PROG 0.41 ;
MODPLA2=VIBR PROC PR2 RIGPLA2 MASPLA2;
*
*------------ Définition des sous-structures ----------
*
SPLA2=STRU RIGPLA2 MASPLA2 ;
CL3=ELST SPLA2 Q3;
*
*---- Définition des liaisons entre sous-structures ---
*
PR=PROG 1 1;
REL1=RELA CL3 UX 1 CLUX2 LX PR ;
REL2=RELA CL3 UY 1 CLUY2 LX PR ;
REL3=RELA CL3 UZ 1 CLUZ2 LX PR ;
REL4=RELA CL3 RX 1 CLRX2 LX PR ;
REL5=RELA CL3 RY 1 CLRY2 LX PR ;
REL6=RELA CL3 RZ 1 CLRZ2 LX PR ;
ENCL=REL1 ET REL2 ET REL3 ET REL4 ET REL5 ET REL6;
*
*--------- Création des bases modales élèmentaires ----
*
BASE1=BASE SPLA1 MODPLA1 ENCL ;
BASE2=BASE SPLA2 MODPLA2 ENCL ;
*
*------------------ Base modale totale ----------------
*------------- correspondant à la réunion des ---------
*----------------- deux bases élémentaires ------------
*
BASET= BASE1 ET BASE2 ;
RIGMO = RIGI BASET ;
MASMO = MASS BASET ;
*
*---------- Recherche de la 1ère fréquence ------------
*---------- propre de la structure totale -------------
*
SOL.3= VIBR PROC (PROG 0.65) MASMO RIGMO ;
FREQ3=TIRE SOL.3 FREQ RANG 1;
*______________________________________________________
* RESULTATS
*______________________________________________________
SAUT PAGE ; SAUT 4 LIGNE ;
MESS 'ON DOIT TROUVER UNE FREQUENCE DE 0.65 HZ';
SAUT 2 LIGNE ;
MESS 'PAR LA PREMIERE METHODE ON TROUVE : ' FREQ1;
MESS 'PAR LA DEUXIEME METHODE ON TROUVE : ' FREQ2;
MESS 'PAR LA TROISIEME METHODE ON TROUVE : ' FREQ3;
TEMPS ;
* CODE FONCTIONNEMENT
REF=0.65;
RESI1=ABS((FREQ1-REF)/REF);
RESI2=ABS((FREQ2-REF)/REF);
RESI3=ABS((FREQ3-REF)/REF);
SI((RESI1 <EG 5E-2) ET (RESI2 <EG 5E-2) ET
(RESI3 <EG 5E-2));
ERRE 0;
SINO;
ERRE 5;
FINSI;
FIN;
Test dyna5 Comments
SPLA1=STRU RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
SPLA2=STRU RIGPLA2 MASPLA2 ;
ELM2=ELST Q2 SPLA1;
ELM3=ELST Q3 SPLA2;
...
CLUX2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQUX2;
CLUY2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQUY2;
CLUZ2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQUZ2;
CLRX2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQRX2;
CLRY2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQRY2;
CLRZ2=CLST SPLA1 BLOQRZ2;
The operator STRU creates an object of STRUCTURE type by indicating
the mass and the rigidity.
The operator ELST creates an object of ELEMSTRU type by indicating the
structure and the point of the interface. This type of object is used
to describe the constraints between sub-structures when the point of the
interface is free.
The operator CLST creates an object of BLOQSTRU type by indicating the
structure and a rigidity of fixing. This type of object is used to
describe the constraints between sub-structures when the point of the
interface is constrained.
 Interface with free points
Interface with free points
PR2=PROG 1. ; PR3=PROG -1. ;
LIUX=RELA ELM2 UX PR2 ELM3 UX PR3;
LIUY=RELA ELM2 UY PR2 ELM3 UY PR3;
LIUZ=RELA ELM2 UZ PR2 ELM3 UZ PR3;
LIRX=RELA ELM2 RX PR2 ELM3 RX PR3;
LIRY=RELA ELM2 RY PR2 ELM3 RY PR3;
LIRZ=RELA ELM2 RZ PR2 ELM3 RZ PR3;
The operator RELA describes elementary constraints between the
sub-structures, it creates an object of ATTACHE type.
The element of structure ELM2 (that is to say Q2 point) has the same
displacements as the element ELM3 (Q3 point).
 Interface with fixed point
Interface with fixed point
PR2=PROG 1. 1.;PR3=PROG 1. 1.;
LIUX=RELA CLUX2 LX PR2 CLUX3 LX PR3;
LIUY=RELA CLUY2 LX PR2 CLUY3 LX PR3;
LIUZ=RELA CLUZ2 LX PR2 CLUZ3 LX PR3;
LIRX=RELA CLRX2 LX PR2 CLRX3 LX PR3;
LIRY=RELA CLRY2 LX PR2 CLRY3 LX PR3;
LIRZ=RELA CLRZ2 LX PR2 CLRZ3 LX PR3;
The fixing of structure CLUX2 (related to Q2 X-displacement) has
the same component as CLUX3. Note that 'LX' is the compulsory component
for a fixing.
BASE1=BASE SPLA1 MODPLA1 ENCL ;
BASE2=BASE SPLA2 MODPLA2 ENCL ;
The operator BASE creates an object of BASEMODA type. This object
contains :
- the structure (SPLA1),
- the mode shapes related to this structure (MODPLA1),
- the constraints (ENCL).
BASET = BASE1 ET BASE2 ;
RIGMO = RIGI BASET ;
MASMO = MASS BASET ;
The two modal bases are joined together.
The operators RIGI and MASS calculate rigidity and mass matrices by using
a modal basis (BASET).