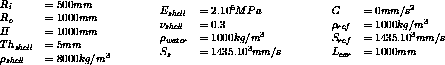
Test name
fsi4
Calculation type
MECHANICS DYNAMICS 2D FOURIER
FLUID-STRUCTURE INTERACTION
Finite element type
COQ2, LQUA4, RACO
Topic
Frequencies of concentric shells coupled by fluid.
Both the concentric shells are separated by a volume of water. Springs are on the bottom of the shells. The inner radius is 0.5m and the outer radius is 1m.
Goal
Find the frequencies of the first and second mode shapes of the shells (M=1).
Reference CASTEM
Report CEA 91/479 : Validation of CASTEM 2000 for fluid structure interaction problems.
Version
97' customer version
Model description
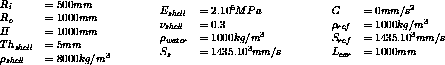
Test fsi4 Results
Results
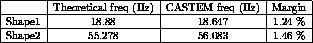
CASTEM figures
* Test Fsi4.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* -------------------------------- *
* *
* CAS TEST DU 91/10/04 PROVENANCE : PETI
OPTI ECHO 0;
SAUT PAGE;
*
*******************************************************
* *
* TEST FSI4 *
* *
* CONCENTRIC SHELLS COUPLED BY FLUID *
* *
* Calculation of the frequencies of two concentric *
* shells with springs coulped by water in between. *
* The inner radius is 0.5m and the outer radius is *
* 1.0m *
* *
* *
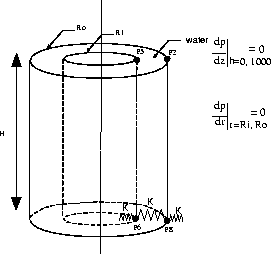
* P5 P7 *
* | | *
* | | *
* | | *
* | fluid | *
* | | *
* | | *
* | | *
* | | *
* ^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^ *
* K P6 K P8 K *
* *
* The boundary conditions are *
* *
* dp | *
* ---- | = 0. *
* dz | h = 0. , 1.0 *
* *
* dp | *
* ---- | = 0. *
* dr | r = Ri , Ro *
*******************************************************
*
TEMPS;
*
OPTI DIME 2;
OPTI MODE FOUR 1 ;
OPTI ELEM QUA4;
*
GRAPH = 'N';
*
*=====================================================*
* geometry *
*=====================================================*
*
* Dimensions en metres
*
* Points
*
N1 = 1 ; N2 = 1 ;
P5 = 500.0 1000.0 ; P6 = 500.0 0.0 ;
P7 = 1000. 1000.0 ; P8 = 1000. 0.0 ;
*
*
*
S5 =P5 D N1 P6 ; S6 = P8 D N1 P7 ;
*
STEEL = S5 ET S6 ;
WATER = (S5 PLUS (2.5 0.)) TRAN N2 (495.0 0. ) ;
RAC1 = RACC 3.0 WATER STEEL ;
*
* OPTIO FOR TRACE
*
SI (NEG GRAPH 'N');
TITR ' FSI4 : MAILLAGE';
TRAC QUAL (WATER ET (0 0));
FINSI;
*
*=====================================================*
* modele - affecte - materiau - rigidite - masse *
*=====================================================*
*
MODCOQ=MODL STEEL MECANIQUE COQ2 ;
MODLIQ=MODL WATER LIQUIDE LQU4;
MODRAC=MODL RAC1 MECANIQUE LIQUIDE RACO;
*
MATCOQ=MATR MODCOQ RHO 8.E-9 YOUN 2.E5 NU 0.3 ;
MATLIQ = MATR (MODLIQ ET MODRAC)
RHO 1.E-9 RORF 1.E-9 CSON 1435.0E3 CREF
1435.0E3 LCAR 1000. G 0.;
CARCOQ=CARB MODCOQ EPAI 5.0 ;
CARRAC=CARB MODRAC LIQU WATER;
MATCOQ=MATCOQ ET CARCOQ;
MATLIQ=MATLIQ ET CARRAC;
*
K =3.7458E4/2.0;
PP =PROG K (-1*K) K ;
PPNEW = PROG K ( -1*K) ( -1*K) K;
RIG1 = RIGI (MODCOQ ET MODLIQ ET MODRAC)
(MATCOQ ET MATLIQ) ;
MAS4 = MASS (MODRAC ET MODLIQ )(MATLIQ) ;
*
*
*=====================================================*
* boundary conditions *
*=====================================================*
*
RES1 = BLOQ UZ RT (S5 ET S6) ;
RIG2 = (APPU UR UT K P8 ) ET (APPU UR UT K P6 ) ;
RIG3 = ( MANU 'RIGI' type 'RIGIDITE' (P6 D 1 P8)
(MOTS UR) PPNEW )
ET ( MANU 'RIGI' type 'RIGIDITE' (P6 D 1 P8)
(MOTS UT) PPNEW );
RIG4 = RIG1 ET RIG2 ET RIG3 ; ;
*
*=====================================================*
* theritical value of frequency
*
FRE1 = TABLE ;
FRE1.1 = 18.88 ;
FRE1.2 = 55.278;
LIST1 = PROG FRE1.1 FRE1.2 ; ;
*
*=====================================================*
* calculation of the frequencies *
* and *
* extraction of some results *
*=====================================================*
*
*
* Use of the operator VIBR. (option PROC)
*
*
RESUL = VIBR PROC LIST1 (RES1 ET RIG4 ) MAS4 ;
*
*=====================================================*
* results *
*=====================================================*
*
MESS ' RESULTATS ';
MESS ' --------- ';
SAUT 1 LIGN;
*
*
FRE2 = TABLE; MOD = TABLE; DEF = TABLE;ERG = TABLE;
*
I = 0;
REPETER BLOC1 2;
I = I + 1;
FRE2.I = TIRE RESUL FREQ RANG I;
ERG.I = 100 * (ABS ((FRE1.I - FRE2.I) / FRE1.I));
MESS ' MODE ' I ;
MESS ' ----------';
MESS ' Frequence theorique :' FRE1.I 'Hz';
MESS ' Frequence calculee :' FRE2.I 'Hz';
MESS ' Soit un ecart de : ' ERG.I '%';
SAUT 1 LIGN;
FIN BLOC1;
*
*=====================================================*
* code validation *
*=====================================================*
*
ERGMAX = MAXI (PROG ERG.1 ERG.2 );
*
SI (ERGMAX <EG 5.);
ERRE 0;
SINON;
ERRE 5;
FINSI;
*
SAUT 1 LIGN;
TEMPS;
SAUT 1 LIGN;
*
FIN;
*
Test fsi4 Comments
WATER = (S5 PLUS (2.5 0.)) TRAN N2 (495.0 0. ) ;
RAC1 = RACC 3.0 WATER STEEL ;
If the distance between points of STEEL and WATER is smaller than 3.0 mm,
the operator RACCORD creates a line of double points by joining the
STEEL structure with the WATER fluid. This corresponds to the creation of
union elements between STEEL and WATER.
Note that there is a clearance between WATER boundaries and STEEL median
line, corresponding here with the thickness of the shell.
MODCOQ=MODEL STEEL MECANIQUE COQ2 ;
MODLIQ=MODEL WATER LIQUIDE LQU4;
MODRAC=MODEL RAC1 MECANIQUE LIQUIDE RACO;
Fluid-structure interaction requires three different models : the liquid, the solid and the model of union elements.
MATLIQ = MATER (MODLIQ ET MODRAC) RHO 1.E-9
RORF 1.E-9 CSON 1435.0E3 CREF 1435.0E3
LCAR 1000. G 0.;
...
CARRAC=CARAC MODRAC LIQU WATER;
The definition of material properties is the same for the liquid model and the union
model.
The liquid model has no geometrical characteristics but the position of the liquid
has to be known : hence the operator CARAC is used with the keyword LIQU to indicate
that the liquid concerning the union elements of MODRAC is represented by the object
WATER.
RIG2 = (APPU UR UT K P8 ) ET (APPU UR UT K P6 ) ;
RIG3 = ( MANU 'RIGI' type 'RIGIDITE' (P6 D 1 P8) (MOTS UR) PPNEW )
ET ( MANU 'RIGI' type 'RIGIDITE' (P6 D 1 P8) (MOTS UT) PPNEW );
Springs can be modelled by two methods :
- with operator APPUI if the spring is connected to a fixed point,
- with operator MANUEL RIGI if the spring joins two points of the structure. In this
case, a stiffness is added to each point.