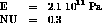
Test name
joi41
Calculation type
ISOTROPIC ELASTIC MECHANICS
Finite element type
QUA4, CUB8,JOI4
Topic
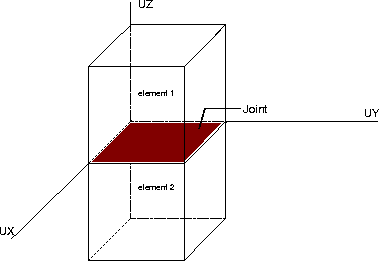
Two superposed cubes with a JOI4 joint in their intersection
We study the effects of joints with the help of two examples: cubes
with joint and cubes without joint.
Goal
Calculate the effect of a JOI4 joint on displacements, strains and stresses.
Version
97' customer version
Model description
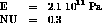
* Test Joi41.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* --------------------------------- *
* *
OPTI ECHO 0;
SAUT PAGE;
*
*******************************************************
* *
* TEST JOI41 *
* *
* 2 CUBES SUPERPOSES AVEC UN JOINT JOI4 *
* AU MILIEU ( JOI4 3D ISOTROPE ) *
* *
* Deux CUB8 sont superposes. On place un joint JOI4 *
* entre les 2 cubes. Les noeuds de la surface infe- *
* -rieure du cube du bas sont encastres. Une force *
* de traction verticale (i.e. suivant z) est exercee *
* sur la surface superieure du cube du haut. *
* Deux cas sont etudies : *
* - 1 / On suppose que le joint n'existe pas entre *
* les deux cubes. *
* - 2 / On suppose que le joint existe et a une *
* raideur normale tres grande par rapport a *
* celle de chacun des cubes. *
* Les deplacements UZ des noeuds des deux cubes *
* doivent etre les memes dans les deux cas. *
* Raideur de chacun des cubes : *
* sigma = force / A A = section *
* or force = k * delta k = raideur *
* delta = deplacement *
* de + sigma = E * epsilon E = Young *
* ou epsilon = delta / L L = hauteur du cube *
* ---> k = E * A / L *
* ---> k = 4.2 E11 *
* On choisit pour raideur du joint, la valeur *
* k = 4.2 E15 *
* *
*******************************************************
*
TEMPS ;
*
SAUT PAGE;
MESS ' ' ;
MESS ' _____________________________________________' ;
MESS '! !' ;
MESS '! CAS DE DEUX CUBES SUPERPOSES SANS JOINT !' ;
MESS '! ENTRE EUX !' ;
MESS '!___________________________________________ !' ;
MESS ' ' ;
*
OPTION DIME 3 ;
OPTION ELEM QUA4 MODE TRID ;
*
* ----DEFINITION DE LA GEOMETRIE DU CUBE SUPERIEUR-----
*
SA1 = 0.00 0.00 0.00 ;
SB1 = 2.00 0.00 0.00 ;
SC1 = 2.00 2.00 0.00 ;
SD1 = 0.00 2.00 0.00 ;
*
* ---------- MAILLAGE ----------
*
SH1 = SA1 DROIT 1 SB1 ;
SH2 = SB1 DROIT 1 SC1 ;
SH3 = SC1 DROIT 1 SD1 ;
SH4 = SD1 DROIT 1 SA1 ;
*
SL1 = SH1 ET SH2 ET SH3 ET SH4 ;
SS1 = SURF SL1 PLAN ;
*
* ----DEFINITION DE LA GEOMETRIE DU CUBE INFERIEUR-----
*
IA1 = 0.00 0.00 -4.00 ;
IB1 = 2.00 0.00 -4.00 ;
IC1 = 2.00 2.00 -4.00 ;
ID1 = 0.00 2.00 -4.00 ;
*
* ---------- MAILLAGE ----------
*
IH1 = IA1 DROIT 1 IB1 ;
IH2 = IB1 DROIT 1 IC1 ;
IH3 = IC1 DROIT 1 ID1 ;
IH4 = ID1 DROIT 1 IA1 ;
*
IL1 = IH1 ET IH2 ET IH3 ET IH4 ;
IS1 = SURF IL1 PLAN ;
*
OPTION ELEM CUB8 ;
*
VOLS = SS1 VOLU 1 TRAN ( 0.00 0.00 -2.00 ) ;
FACS = FACE 2 VOLS ;
VOLI = IS1 VOLU 1 TRAN ( 0.00 0.00 2.00 ) ;
FACI = FACE 2 VOLI ;
VT1 = VOLS ET VOLI ;
VT1 = ELIM 0.00001 VT1 ;
VTSAN = VT1 ;
*
* ------- DEFINITION DES CONDITIONS AUX LIMITES -------
*
CL11 = BLOQ IC1 UX ;
CL12 = BLOQ IC1 UY ;
CL13 = BLOQ IC1 UZ ;
CL1 = CL11 ET CL12 ET CL13 ;
*
CL21 = BLOQ IH2 UX ;
CL22 = BLOQ IH2 UZ ;
CL2 = CL21 ET CL22 ;
*
CL31 = BLOQ IH3 UY ;
CL32 = BLOQ IH3 UZ ;
CL3 = CL31 ET CL32 ;
*
CL4 = BLOQ IA1 UZ ;
*
CL = CL1 ET CL2 ET CL3 ET CL4 ;
*
* ---------- DEFINITION DU MODELE ----------
*
MOD1 = MODL VT1 'MECANIQUE' 'ELASTIQUE' 'ISOTROPE' ;
MA1 = MATR MOD1 YOUN 2.1E11 NU 0.3 ;
*
* ---------- MATRICE DE RIGIDITE ----------
*
RI1 = RIGI MOD1 MA1 ;
RI2 = RI1 ET CL ;
*
* ---------- PRESSION UNIFORME ----------
*
CHPO1= PRES 'MASS' MOD1 -100000.00 SS1 ;
*
* ---------- RESOLUTION ----------
*
RE = RESO RI2 CHPO1 ;
*
* ------REDUC. DES DEPLA. AUX DIFFERENTS ELEMENTS------
*
DEPS = REDU RE VOLS ;
MESS ' DEPLACEMENTS DES NOEUDS DU CUBE SUPERIEUR ' ;
LIST DEPS;
*
desusa=deps;
*
DEPI = REDU RE VOLI ;
MESS ' DEPLACEMENTS DES NOEUDS DU CUBE INFERIEUR ' ;
LIST DEPI ;
*
deinsa=depi;
*
*
* ---------- CALCUL DES DEFORMATIONS ----------
*
EPS1 = EPSI MOD1 RE ;
*
* ------REDUC. DES DEFOR. AUX DIFFERENTS ELEMENTS------
*
EPSS = REDU EPS1 VOLS ;
MESS ' DEFORMATIONS DU CUBE DU HAUT ' ;
LIST EPSS ;
*
EPSB = REDU EPS1 VOLI ;
MESS ' DEFORMATIONS DU CUBE DU BAS ' ;
LIST EPSB ;
*
* ------- CALCUL DES CONTRAINTES --------
*
SIG1 = SIGMA MOD1 MA1 RE ;
*
* -----REDUC. DES CONTR. AUX DIFFERENTS ELEMENTS-------
*
SIGS = REDU SIG1 VOLS ;
MESS ' CONTRAINTES DU CUBE DU HAUT ' ;
LIST SIGS ;
*
SIGI = REDU SIG1 VOLI ;
MESS ' CONTRAINTES DU CUBE DU BAS ' ;
LIST SIGI ;
*
MESS ' ' ;
MESS ' ' ;
MESS' *=============================================*';
*
SAUT PAGE;
MESS ' ' ;
MESS ' ' ;
MESS ' _____________________________________________' ;
MESS '! !' ;
MESS '! CAS DE DEUX CUBES SUPERPOSES AVEC UN !' ;
MESS '! JOINT ENTRE EUX !' ;
MESS '!____________________________________________!' ;
MESS ' ' ;
MESS ' ' ;
*
*
OPTION DIME 3 ;
OPTION ELEM QUA4 MODE TRID ;
*
* -----DEFINITION DE LA GEOMETRIE DU CUBE SUPERIEUR----
*
SA1A = 0.00 0.00 0.00 ;
SB1A = 2.00 0.00 0.00 ;
SC1A = 2.00 2.00 0.00 ;
SD1A = 0.00 2.00 0.00 ;
*
* ---------- MAILLAGE ----------
*
SH1A = SA1A DROIT 1 SB1A ;
SH2A = SB1A DROIT 1 SC1A ;
SH3A = SC1A DROIT 1 SD1A ;
SH4A = SD1A DROIT 1 SA1A ;
*
SL1A = SH1A ET SH2A ET SH3A ET SH4A ;
SS1A = SURF SL1A PLAN ;
*
* ----DEFINITION DE LA GEOMETRIE DU CUBE INFERIEUR-----
*
IA1A = 0.00 0.00 -4.00 ;
IB1A = 2.00 0.00 -4.00 ;
IC1A = 2.00 2.00 -4.00 ;
ID1A = 0.00 2.00 -4.00 ;
*
* ---------- MAILLAGE ----------
*
IH1A = IA1A DROIT 1 IB1A ;
IH2A = IB1A DROIT 1 IC1A ;
IH3A = IC1A DROIT 1 ID1A ;
IH4A = ID1A DROIT 1 IA1A ;
*
IL1A = IH1A ET IH2A ET IH3A ET IH4A ;
IS1A = SURF IL1A PLAN ;
*
OPTION ELEM CUB8 ;
*
VOLSA = SS1A VOLU 1 TRAN ( 0.00 0.00 -2.00 ) ;
FACSA = FACE 2 VOLSA ;
VOLIA = IS1A VOLU 1 TRAN ( 0.00 0.00 2.00 ) ;
FACIA = FACE 2 VOLIA ;
VT1A = VOLSA ET VOLIA ;
*
* ------ DEFINITION DES CONDITIONS AUX LIMITES --------
*
CL11A = BLOQ IC1A UX ;
CL12A = BLOQ IC1A UY ;
CL13A = BLOQ IC1A UZ ;
CL1A = CL11A ET CL12A ET CL13A ;
*
CL21A = BLOQ IH2A UX ;
CL22A = BLOQ IH2A UZ ;
CL2A = CL21A ET CL22A ;
*
CL31A = BLOQ IH3A UY ;
CL32A = BLOQ IH3A UZ ;
CL3A = CL31A ET CL32A ;
*
CL4A = BLOQ IA1A UZ ;
*
CLA = CL1A ET CL2A ET CL3A ET CL4A ;
*
* ---- DEFINITION DU MODELE DES DEUX CUBES ----
*
MOD1A = MODL VT1A 'MECANIQUE' 'ELASTIQUE' 'ISOTROPE' ;
MA1A = MATR MOD1A YOUN 2.1E11 NU 0.3 ;
*
* - CREATION DE L'ELEMENT JOINT ENTRE LES DEUX CUBES -
*
OPTION ELEM LIA4 ;
VOLJA = LIAISON 0.0001 FACSA FACIA ;
*
VTOTAL=VT1A ET VOLJA ;
*
* ---------- DEFINITION DU MODELE DU JOINT ----------
*
MODJA = MODL VOLJA 'MECANIQUE' 'ELASTIQUE' 'ISOTROPE'
JOI4 ;
MAJA = MATR MODJA KS 4.2E15 KN 4.2E15 ;
*
* ----- MODELE ET MATERIAU DE TOUTE LA STRUCTURE ------
*
MODTA = MOD1A ET MODJA ;
MATTA = MA1A ET MAJA ;
*
* ---------- MATRICE DE RIGIDITE ----------
*
RITA = RIGI MODTA MATTA ;
RITOA = RITA ET CLA ;
*
* ---------- PRESSION UNIFORME ----------
*
CHPO1A= PRES 'MASS' MODTA -100000.00 SS1A ;
*
* ---------- RESOLUTION ----------
*
RETA = RESO RITOA CHPO1A ;
*
* ----- REDUC. DES DEPLA. AUX DIFFERENTS ELEMENTS -----
*
DEPSA = REDU RETA VOLSA ;
MESS ' DEPLACEMENTS DES NOEUDS DU CUBE SUPERIEUR ' ;
LIST DEPSA;
*
DEPIA = REDU RETA VOLIA ;
MESS ' DEPLACEMENTS DES NOEUDS DU CUBE INFERIEUR ' ;
LIST DEPIA ;
*
DEPJ = REDU RETA VOLJA ;
MESS ' DEPLACEMENTS DES NOEUDS DU JOINT ' ;
LIST DEPJ;
* ---------- CALCUL DES DEFORMATIONS ----------
*
EPSTA = EPSI MODTA RETA ;
*
* ---- REDUC. DES DEFOR. AUX DIFFERENTS ELEMENTS ------
*
EPSSA = REDU EPSTA VOLSA ;
MESS ' DEFORMATIONS DU CUBE DU HAUT ' ;
LIST EPSSA ;
*
EPSBA = REDU EPSTA VOLIA ;
MESS ' DEFORMATIONS DU CUBE DU BAS ' ;
LIST EPSBA ;
*
EPSJA = REDU EPSTA VOLJA ;
MESS ' DEFORMATIONS DU JOINT ' ;
LIST EPSJA ;
*
* ---------- CALCUL DES CONTRAINTES ----------
*
SIGTA = SIGMA MODTA MATTA RETA ;
*
* ----- REDUC. DES CONTR. AUX DIFFERENTS ELEMENTS -----
*
SIGSA = REDU SIGTA VOLSA ;
MESS ' CONTRAINTES DU CUBE DU HAUT ' ;
LIST SIGSA ;
*
SIGIA = REDU SIGTA VOLIA ;
MESS ' CONTRAINTES DU CUBE DU BAS ' ;
LIST SIGIA ;
*
SIGJA = REDU SIGTA VOLJA ;
MESS ' CONTRAINTES DU JOINT ' ;
LIST SIGJA ;
*
* ---------- CODE DE FONCTIONNEMENT ----------
*
*
desuav=deps;
* difference des deplacements configurations avec/sans
* joint pour les cubes superieurs
desdif=desusa-desuav;
*
deinav=depi;
* difference des deplacements configurations avec/sans
* joint pour les cubes inferieurs
deidif=deinsa-deinav;
*
maxdis = maxi desdif 'ABS' ;
maxdii = maxi deidif 'ABS' ;
*
*
si ((maxdis <eg 1e-9) et (maxdii <eg 1e-9));
erre 0 ;
sino ;
erre 5 ;
finsi ;
*
*
FIN;
Test joi41 Comments
OPTI ELEM LIA4 ; VOLJA = LIAISON 0.0001 FACSA FACIA ;The LIAISON operator generates the set of linkage elements between two surfacic objects (FACSA and FACIA: MAILLAGE type). VOLJA is the generated object (MAILLAGE type), and 0.0001 is the proximity criterion between the two surfacic objects.
DEPS = REDU RE VOLS ; (OBJET3 = REDU OBJET1 OBJET2 ;)The REDU operator restricts :
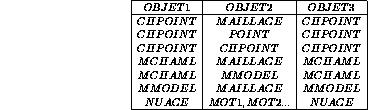
In case of restriction of a MCHAML or a MMODEL on a mesh :
- this mesh must be composed of elements of the same type
as the mesh that supports the MCHAML or the MMODEL
- all the elements of the mesh must be included in the
mesh that supports the MCHAML or the MMODEL