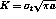
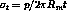
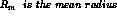
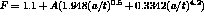
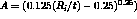
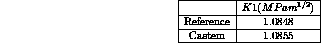
For this problem the CASTEM solution for the stress factor K is given by the relation ship :
Test name
rupt1
Calculation type
MECHANICS ELASTIC-PLASTIC AXI
Finite element type
QUA8
Topic
STRESS INTENSITY FACTOR IN LINEAR MECHANICS ELASTIC OF A SOLID CYLINDER WITH A CIRCUMFERENCIAL CRACK
The structure is a solid cylinder with a circumferencial crack subjected to tensile stress. The goal is
to calculate the Crack Opening Displacement (COD) at the crack tip and the stress factor
in linear elastic mechanics of this structure. The theoreticals values are given by the relationships :
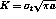
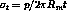
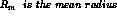
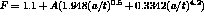
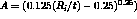
For this problem the CASTEM solution for the stress factor K is given by the relation ship :
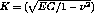
Reference CASTEM
Test NAFEMS : Ductile Fracture Handbook, A. ZAHOOR, EPRI, 1990 : rupt1 Modélisation des structures élastiques dans CASTEM 2000.
Version
97' customer version
Model description
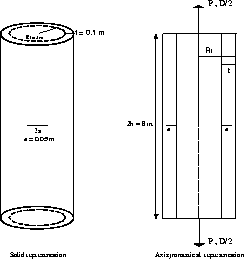
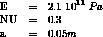
Test rupt1 Results
RESULTS
CASTEM FIGURES
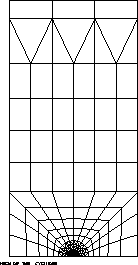
* Test Rupt1.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* --------------------------------- *
* *
OPTION ECHO 0;
GRAPH = 'N';
SAUT PAGE;
*******************************************************
*
* QUALIFICATION DU CALCUL DE K EN
* ELASTICITE LINEAIRE SUR UN CYLINDRE AVEC
* UNE FISSURE DEBOUCHANTE CIRCONFERENTIELLE
*
* Le calcul est compare a celui obtenu par A ZAHOOR
*******************************************************
* R = rayon interne de la tuyauterie (M)
* B = épaisseur de la tuyauterie (M)
* L = longueur de la tuyauterie (M)
* A = longueur de la fissure (M)
* MYOU = module d'Young (Pa)
* TA = chargement appliqué (N)
***
TA = 1.E6;
R = 1.;
B = 0.1;
A = B / 2.;
L = R * 4.;
MYOU = 2.0E11;
***
*** Maillage
***
OPTION DIME 2 ELEM QUA8 MODE AXIS;
t = a / 100.; densite t ; pf = (a 0.);
c1 = (c ( pf moin (t 0.)) pf ( pf plus (0. t)))
c pf ( pf plus (t 0.));
sf = cout pf c1;
r1 = t ; rr1 = t;
repeter bhomo 7;
ri = r1 + ( 0.3 * r1 );
rri = rr1 + ri; dens ri;
ci = (c (pf moin (rri 0.)) pf ( pf plus (0. rri)))
c pf (pf plus (rri 0.));
sf = sf et (cout c1 ci);
c1 = ci ; r1 = ri ; rr1 = rri;
fin bhomo;
dens (a / 3.);
p0 = (0. 0.) ; p1 = (b 0.);
p2 = p0 plus (0. a) ; p3 = p1 plus (0. a);
pi1 = ci poin 1 ; l1 = pi1 d p0 ; n = (nbel l1) * -1;
pi2 = ci poin 4 ; l2 = pi2 d n p2;
pi3 = ci poin 10 ; l3 = pi3 d n p3;
pi4 = ci poin 13 ; l4 = pi4 d p1;
ci = inve ci ; ligh = p2 d p3;
sc1 = dall l1 (p0 d p2) (inve l2) (ci comp pi2 pi1);
sc2 = dall l2 ligh (inve l3) (ci comp pi3 pi2);
sc3 = dall l3 (p3 d p1) (inve l4) (ci comp pi4 pi3);
sc = sc1 et sc2 et sc3;
dens (a / 2.);
mrest1 = ligh tran (0. (2.*a)) dini (40*t) dfin (50*t);
l1 = mrest1 cote 3;
YY1 = coor 2 (point l1 init);
l2 = D 3 (B (YY1 + (0.7*a))) (0. (yy1 + (0.7*a)));
S1 = COUT L1 L2;
YY1 = COOR 2 (l2 point init);
mrest2 = l2 tran (0. (L - YY1)) dini (80*t)
dfin (150*t);
sut = sf et sc et mrest1 et S1 et mrest2;
ELIM 1.E-8 SUT;
DEPL PLUS SUT (R 0.);
L1 = (CONT SUT) ELEM APPU (SUT POIN
DROI (R 0.) ((B + R) 0.) 1.E-8);
L2 = (CONT SUT) ELEM APPU (SUT POIN
DROI ((B + R) 0.) ((B + R) L) 1.E-8);
L3 = (CONT SUT) ELEM APPU (SUT POIN
DROI ((B + R) L) (R L) 1.E-8);
L4 = (CONT SUT) ELEM APPU (SUT POIN
DROI (R L) (R 0.) 1.E-8);
L5 = (CONT SUT) COMP P1 PF;
SI ( NEG GRAPH 'N' );
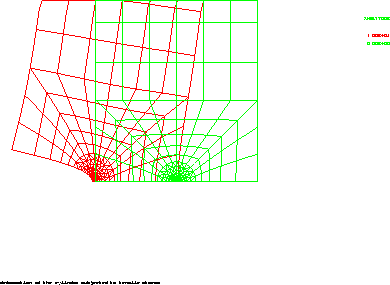
TITR 'MAILLAGE DU CYLINDRE';
TRAC sut;
FINSI;
******
****** RESOLUTION EN ELASTICITE LINEAIRE
******
MO1 = MODELE SUT MECANIQUE ELASTIQUE
PLASTIQUE ISOTROPE;
MA1 = MATER MO1 YOUNG MYOU NU 0.3 TRAC COUTRAC;
RI = (BLOQ UZ L5) ET (RIGI MA1 MO1);
AIR1 = PI*(((R + B)**2.) - (R*R));
FOR1 = PRES 'MASS' MO1 (0. - (TA/AIR1)) L3;
DEP1 = RESO FOR1 RI;
SIG1 = SIGMA MO1 MA1 DEP1;
SI ( NEG GRAPH 'N' );
TITR 'DEFORMATION DU CYLINDRE SOUS TRACTION UNIFORME';
TRAC (DEFO SUT DEP1);
FINSI;
***
*** Solution COD (MM) et K (MPA M^0.5) de castem
***
COD_CAL = (EXTR DEP1 'UZ' P1)*2000.;
SUPTAB = TABLE ;
SUPTAB.'OBJECTIF' = MOT 'J';
SUPTAB.'LEVRE_SUPERIEURE' = l1 diff l5;;
SUPTAB.'FRONT_FISSURE' = PF ;
SUPTAB.'MODELE' = MO1;
SUPTAB.'CARACTERISTIQUES' = ma1;
SUPTAB.'SOLUTION_RESO' = dep1;
SUPTAB.'CHARGEMENTS_MECANIQUES' = for1;
SUPTAB.'COUCHE' = 5;
G_THETA SUPTAB;
K_CAL = (MYOU*(SUPTAB.'RESULTATS')/(1 - (0.3**2)))**0.5;
K_CAL = K_CAL*1.E-6;
***
*** Solution Analytique Zahoor
***
RAP1 = R / B;
SI (RAP1 < 10.); GRANDA = ((0.125*RAP1) - 0.25)**0.25;
FINSI;
SI (RAP1 >EG 10.); GRANDA = ((0.4*RAP1) - 3.00)**0.25;
FINSI;
F = (1.9480*((A/B)**1.5)) + (0.3342*((A/B)**4.2));
F = 1.1 + (GRANDA*F);
SIGT = TA / AIR1;
K_ZAH = SIGT*((PI*A)**0.5)*F;
K_ZAH = K_ZAH*1.E-6;
ERR1 = abs ((K_CAL - K_ZAH)/K_ZAH);
MESS ' Facteur K CASTEM =' K_CAL '(Mpa.M^0.5)';
MESS ' Facteur K ZAHOOR =' K_ZAH '(Mpa.M^0.5)';
MESS ' Erreur relative =' ERR1;
SI (ERR1 < 1.E-2);
ERRE 0;
SINO;
ERRE 5;
FINSI;
FIN;
Test rupt1 Comments
t = a / 100.; densite t; pf = (a 0.);
c1 = (c ( pf moin (t 0.)) pf ( pf plus (0. t)))
c pf ( pf plus (t 0.));
trac c1 ;
sf = cout pf c1;
Thus, the COUT operator constructs a surface which connects two lines or a line and point by means of triangles.
here pf is a point (POINT type) to be connected to the line c1 (line between which the surface is generated (MAILLAGE
type).
SUPTAB = TABLE ; SUPTAB.'OBJECTIF' = MOT 'J'; SUPTAB.'LEVRE_SUPERIEURE' = l1 diff l5; SUPTAB.'FRONT_FISSURE' = PF ; SUPTAB.'MODELE' = MO1; SUPTAB.'CARACTERISTIQUES' = ma1; SUPTAB.'SOLUTION_RESO' = dep1; SUPTAB.'CHARGEMENTS_MECANIQUES' = for1; SUPTAB.'COUCHE' = 5; G_THETA SUPTAB; K_CAL = (MYOU*(SUPTAB.'RESULTATS')/(1 - (0.3**2)))**0.5; K_CAL = K_CAL*1.E-6;The G_THETA procedure has two objectives :
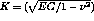 :
:
K_CAL = (MYOU*(SUPTAB.'RESULTATS')/(1 - (0.3**2)))**0.5; K_CAL = K_CAL*1.E-6;