Test name
elas1
Calculation type
MECHANICS ELASTICITY 2D AXI
Finite element type
COQ2
Topic
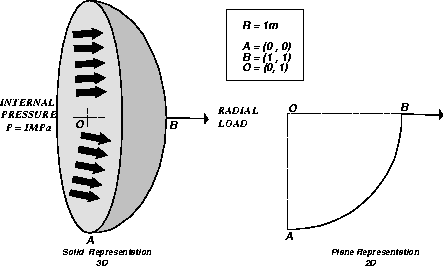
A spherical skullcap subjected to different types of load.
The spherical skullcap is subjected to an internal pressure, to its own weight and
to a radial load. To solve this problem, we use the principle of superposition.
The equivalent loads for each load were calculated and then added before the
resolution of the system.
Goal
Find the radial displacement at a given point B (1,1).
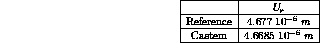
Reference CASTEM
Test NAFEMS : ME1 : Modélisation des structures élastiques dans CASTEM 2000.
Version
97' customer version
Model description


Test elas1 Results
RESULTS
CASTEM FIGURES
* Test Elas1.dgibi: Jeux de données * * --------------------------------- * * GRAPH='N'; SAUT PAGE ; OPTI ECHO 1; * ******************************************************* * TEST ELAS1 * * Une calotte sph}rique est soumise : * - @ une pression interne * - @ son poids propre * - @ une force radiale en tete * * En élasticité et en supposant le probleme * axisymétrique, on se propose de calculer le * déplacement radial en tete de la calotte. * * Pour résoudre ce probleme on utilise le principe * de superposition. Les forces équivalentes pour chaque * chargement sont calculées puis ajoutées avant de * résoudre le systeme. * * Le déplacement radial en tete calculé est comparé à * la valeur théorique égale à 4.677 microns. * ******************************************************* * TITRE 'CALOTTE SPHERIQUE SOUS PLUSIEURS TYPES DE CHARGEMENT'; OPTION DIME 2 ELEM SEG2 MODE AXIS ; GRAPH='N'; * *------------------ DEFINITION DE LA GEOMETRIE -------- * * A = 0 0 ; B = 1 1 ; O = 0 1 ; * L1 = CERC 100 A O B ; * SI (NEG GRAPH 'N'); TRACE L1 ; FINSI; * *----- DEFINITION DES CONDITIONS AUX LIMITES --------- * CL1 = BLOQ B UZ ; CL2 = BLOQ A UR ; CL = CL1 ET CL2 ; * * DEFINITION DU MODELE, DU MATERIAU * ET DES CARACTERISTIQUES * MO = MODL L1 MECANIQUE ELASTIQUE COQ2 ; MA = MATR MO YOUN 2.1E11 NU 0.3 RHO 7.85E4 ; CA = CARB MO EPAI 0.02 ; MA=MA ET CA; * *------- CALCUL DE LA MATRICE DE RIGIDITE ------------- * RI1 = RIGI MO MA ; RI2 = RI1 ET CL ; * *-------------- DEFINITION DES CHARGES ---------------- * * * *------------ PRESSION INTERNE UNIFORME --------------- * FO1 = PRES COQU MO -10000 NORM ; * * -- POIDS PROPRE (IL FAUT CALCULER LA MATRICE MASSE) - * MAS = MASSE MO MA; EL1 = CHANGE L1 POI1 ; POP = MANU CHPO EL1 1 UZ -1 ; FO2 = MAS*POP ; * *------------- FORCE RADIALE EN TETE ------------------ * F=1000*2*PI; FO3 = FORC FR F B ; * FO = FO1 + FO2 + FO3 ; * *--CALCUL PAR RESO DES DEPLACEMENTS ET POST-TRAITEMENT- * RE = RESO RI2 FO ; DR = EXTR RE UR B ; DR = 1000000*DR ; SAUT PAGE ; SAUT 2 LIGN ; MESS ' DEPLACEMENT RADIAL EN TETE THEORIQUE CALCULE ' ; MESS ' UR=4.677 MICRON UR =' DR 'MICRON'; TEMPS ; *--------- CODE DE BON FONCTIONNEMENT ----------------- ERR=100*(ABS(4.677 -DR)/4.677); SI (ERR < 5); ERRE 0; SINON; ERRE 5; FINSI; FIN;
Test elas1 Comments
RI1 = RIGI MO MA ;
RI2 = RI1 ET CL ;
MAS = MASSE MO MA;
The operators RIGI and MASS require the mechanical model (here MO)
and the material and geometrical characteristics (here MA).
For the shell elements it is necessary to define the thickness (EPAI)
FO1 = PRES COQU MO -10000 NORM ;
The operator PRES(SION) calculates the nodal forces equivalent to a pressure. The keyword COQU indicates that the pressure is applied on shell elements.
The operator requires the model (MO) and the value of the pressure.
The keyword NORM(AL) indicates that the pressure is positive when it is carried by a vector perpendicular to the element, oriented positively.
MAS = MASSE MO MA;
EL1 = CHANGE L1 POI1 ;
POP = MANU CHPO EL1 1 UZ -1 ;
FO2 = MAS*POP ;
There are no operators to calculate the own weight. The solution is to multiply the mass matrix (MAS) by an object of CHPOINT type (POP). The POP object defines the value of gravity (direction UZ and value -1).
F=1000*2*PI;
FO3 = FORC FR F B ;
The operator FORCE calculates a force field which is given as a localized force.
Here the force is defined by its component FR, its value F and the geometry on wich it is applied (point B).
FO = FO1 + FO2 + FO3 ;
The three loads are objects of CHPOINT type. It is also possible to add them in order to get the complete load.