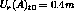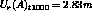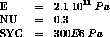Next: Test plas4 Description
Up: PLASTICITY
Previous: Test plas1 Description
Test name
plas2
Calculation type
MECHANIC PLASTICITY 2D AXI
Finite element type
COQ4
Topic
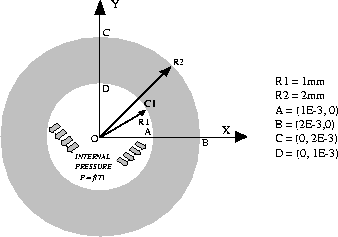
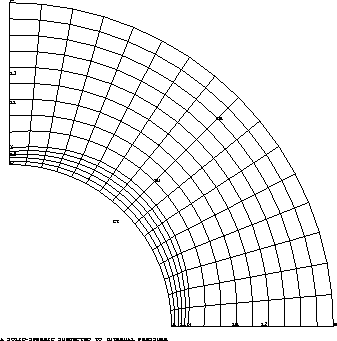
A Spheric-Solid, subjected to an internal pressure.
The structure is a Hollow-Spheric-Solid subjected to an internal pressure. The geometry is axisymetrical,
the inner radius is R1 = 1mm and the outer radius is R2 = 2mm.
The internal pressure P varies as a function of time :
at 0s P = 100 MPa and at 1000s 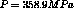
This non linear evolution (resulting from the material) responds in a plastic manner
up to
R = 1.5 mm. time (T).
Goal
Find the computed radial displacements 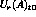 and
and 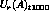 The theoretical values
are :
The theoretical values
are :
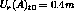
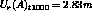
Reference CASTEM
Test NAFEMS : Analytical-Solution : MP2 Modélisation des structures élastiques dans CASTEM 2000.
Version
97' customer version
Model description
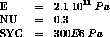
Test plas2 Results
RESULTS
CASTEM FIGURES
* Test Plas2.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* --------------------------------- *
* *
OPTION ECHO 1;
GRAPH='N';
SAUT PAGE ;
*******************************************************
* TEST PLAS2
*
* Sortie du domaine élastique et phase plastique
* (comportement élasto-plastique parfait)
* Calcul axisymétrique avec prise en compte des
* symétries.
*
* Une sphère de rayon extérieur égal à 2 mm et de rayon
* intérieur égal à 1 mm (centre O et contour ABCD) est
* soumise à une pression interne.
*
* La pression évolue en fonction du temps de 100 MPa à
* 0 s jusqu'à 358.9 MPa à 1000 s.
*
* Cette évolution de la pression entraine un
* comportement plastique jusqu'en R=1.5 mm.
*
* Les déplacements radiaux à 0 s et à 1000 s
* sont comparés aux valeurs théoriques (0.4 microns
* et 2.83 microns)
*
*******************************************************
TITRE 'PLAS2 - SPHERE SOUS PRESSION INTERNE';
OPTION DIME 2 ELEM QUA4 MODE AXIS ;
GRAPH='N';
TEMPS ;
*
*------------- Définition de la géométrie -------------
*
O = 0 0 ;
A = 1E-3 0 ;
B = 2E-3 0 ;
C = 0 2E-3 ;
D = 0 1E-3 ;
*
*------------------------------------------------------
* La peau interne est maillée de façon plus fine pour
* un meilleur calcul des contraintes radiales, les
* points X et Y sont introduits à cet effet.
*------------------------------------------------------
*
X = 1.1E-3 0 ;
Y = 0 1.1E-3 ;
*
L1 = A DROIT 5 X ;
L2 = X DROIT 9 B ;
LR = L1 ET L2 ;
CE = CERC 16 B O C ;
L3 = C DROIT 9 Y ;
L4 = Y DROIT 5 D ;
LZ = L3 ET L4 ;
CI = CERC 16 D O A ;
*
SU = LR CE LZ CI DALL PLAN ;
*
SI (NEG GRAPH 'N');
TRACE SU ;
FINSI;
*
*------ Définition des conditions aux limites --------
*----------- (conditions de symétrie) -----------------
*
CL1 = BLOQ LR UZ ;
CL2 = BLOQ LZ UR ;
CL = CL1 ET CL2 ;
*
*--------- Utilisation de la procedure PASAPAS --------
*-- Les objets utilisés par la procédure PASAPAS sont -
*--------- définis dans les lignes qui suivent --------
*
MO= MODL SU MECANIQUE ELASTIQUE PLASTIQUE PARFAIT QUA4;
*
*-----------------------------
* SIGY est la limite élastique
*-----------------------------
*
*------------- Définition du matériau -----------------
*
MAT1 = MATR MO YOUN 2E11 SIGY 300E6 NU 0.3;
*
*------ Définition en Pa de la pression unitaire ------
*
FO = PRES MASS MO 1E6 CI ;
*
*---------- au pas de temps T, la pression vaut F(T)*FO
*
LI1 = PROG 0. 1000. ;
LI2 = PROG 0. 1000. ;
EV = EVOL MANU T LI1 F(T) LI2 ;
CHA1 = CHAR MECA FO EV ;
*
*-- Liste des pas de calcul, 100. MPa est la pression -
*--- de début de plastification, 358.9 MPa engendre --
*----- un comportement plastique jusqu'en R=1.5 mm ----
*
LIS1 = PROG 100. 358.9 ;
TAB1 = TABLE ;
TAB1.'BLOCAGES_MECANIQUES' = CL;
TAB1.'MODELE' = MO;
TAB1.'CARACTERISTIQUES' = MAT1;
TAB1.'CHARGEMENT' = CHA1;
TAB1.'TEMPS_CALCULES' = LIS1;
PASAPAS TAB1 ;
*
*-------- Calcul et impression des résultats ----------
*
RE1 = (TAB1.DEPLACEMENTS.1) ;
RE2 = (TAB1.DEPLACEMENTS.2) ;
*
V1 = EXTR RE1 UR A ;
V1 = 1E6*V1 ;
V2 = EXTR RE2 UR A ;
V2 = 1E6*V2 ;
*
SAUT PAGE ; SAUT 2 LIGN ;
*
MESS ' EN R=1MM : DEPLACEMENT THEORIQUE
CALCULE' ;
SAUT 2 LIGN ;
MESS 'INCREMENT ELASTIQUE UR= 0.40 MICRONS
UR= 'V1 'MICRON';
SAUT 1 LIGN ;
MESS 'INCREMENT PLASTIQUE UR= 2.83 MICRONS
UR= 'V2 'MICRON';
TEMPS ;
*------------ Code de fonctionnement ------------------
ERR1=100*(ABS(0.4 - V1)/0.4);
ERR2=100*(ABS(2.83 - V2)/2.83);
LIST1=PROG ERR1 ERR2;
ERRMAX=MAXI (PROG ERR1 ERR2);
SI (ERRMAX < 5);
ERRE 0;
SINON;
ERRE 5;
FINSI;
FIN;
Test plas2 Comments
LOAD DEFINITION RESULTING FROM AN INTERNAL PRESSURE
FO = PRES MASS MO 1E6 CI ;
The PRES operator calculates the forces which are equivalent to a pressure applied on an object.
Here this operator is connected to key word MASS, referring to the type of solid element on which
the pressure is applied.
MO is the object on which the pressure is applied (MMODEL type) and 1E6 is a pressure algebraic
value (FLOTTANT type). CI is the mesh on which the pressure is applied (MAILLAGE type).
For solid elements, such as those used in this problem, the pressure is assumed to be directed towards
the inside of the solid. In case of a depression, it is required that a field of a negative
pressure points have to be supplied.
LI1 = PROG 0. 1000. ;
LI2 = PROG 0. 1000. ;
EV = EVOL MANU T LI1 F(T) LI2 ;
CHA1 = CHAR MECA FO EV ;
EV is time description of the loading (EVOLUTION type) function containing in abscissa the times
(in chronological order) and in ordinate the values F(T) of the function F for each value of the times T.
Thus, The CHAR operator constructs a CHAR1 object of CHARGEMENT type, of FORCE subtype which contains the space and time description
of the equivalent loading.




Next: Test plas4 Description
Up: PLASTICITY
Previous: Test plas1 Description
ven 3 nov 04:14:58 NFT 2000
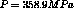
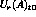 and
and 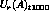 The theoretical values
are :
The theoretical values
are :