Goal
Find the strength multipliers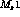 and
and 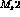 .
.
Test name
four1
Calculation type
MECHANICS BUCKLING. 2D FOURIER
Finite element type
COQ2
Topic
Endless cylinder under external pressure.
This test simulates an endless cylinder subjected to an external pressure.
The first natural frequency of the structure's second mode shape is determined by a Fourier analysis. This result is used to make a buckling analysis.
Goal
Find the strength multipliers 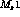 and
and 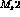 .
.
Reference
Analytic solution.
Version
97' customer release
Model description
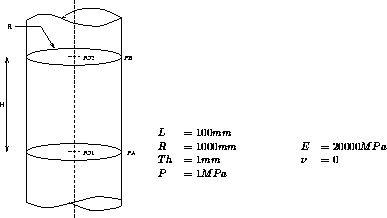
Test four1 Results
Results

CASTEM figures
* Test Four1.dgibi: Jeux de données * * --------------------------------- * * * OPTION ECHO 0; GRAPH='N'; SAUT PAGE ; ******************************************************* * TEST FOUR1 * * CYLINDRE INFINI SOUS PRESSION EXTERNE(NU=0) * * Soit un cylindre infini soumis à une pression externe * * Par une analyse de Fourier, on se propose de * déterminer la première fréquence propre du deuxième * mode de la structure. * * On utilise le résultat pour effectuer une analyse * de flambage. * ******************************************************* * TITRE 'CYLINDRE INFINI SOUS PRESSION EXTERNE'; OPTI DIME 2 ELEM SEG2 MODE FOUR 0; GRAPH='N'; TEMPS ; * *----------- CONSTRUCTION DE LA GEOMETRIE ------------- * PA=1000. 0.;PB=1000. 100.;PO1=0. 0.;PO2=0. 100.; CYL=PA D 4 PB; * SI (NEG GRAPH 'N'); TRAC ECLA ELEM CYL; FINSI; * MOD1=MODL CYL MECANIQUE ELASTIQUE COQ2; * *--- DECLARATION DE FOURIER NOHARM POUR LES OBJETS ---- *------- QUI SERONT UTILISES POUR PLUSIEURS ---------- *--------------- NUMEROS D'HARMONIQUE ----------------- * OPTI MODE FOUR NOHARM; * * *-------- CONDITIONS AUX LIMITES SYMETRIQUES ---------- * SYMB=SYMT CYL DEPL ROTA PA PO1 0.5; SYMH=SYMT CYL DEPL ROTA PB PO2 0.5; CDL=SYMB ET SYMH; * *----------- MATERIAU ET CARACTERISTIQUES ------------- * PP = MANU CHPO CYL 1 P 1. ; MAT =MATR MOD1 YOUN 20000. NU 0.; CAR=CARB MOD1 EPAI 1.; MAT=MAT ET CAR; * *----------- DECLARATION DE FOURIER MODE 0 ------------ *----------- POUR LE CALCUL DES CONTRAINTES ----------- * OPTI MODE FOUR 0; FP=PRES COQU MOD1 1. NORM ; RIG=RIGI MOD1 MAT; * RIGADD = RIGI UT 1.E-4 PA ; * AAA = RIG ET CDL ET RIGADD ; U=RESO AAA FP ; SIG=SIGMA U MOD1 MAT; * *----------- DECLARATION DE FOURIER MODE 2 ------------ *------------ POUR L'ANALYSE DE FLAMBAGE -------------- * OPTI MODE FOUR 2; * PP = MANU CHPO CYL 1 P 1. ; * MKSI=KSIGMA MOD1 MAT (SIG * -1.) FLAM; RIG=RIGI MOD1 MAT ; * *------- RECHERCHE DE LA 1ERE FREQUENCE PROPRE -------- * MODF=VIBR PROC (PROG 0.) (RIG ET CDL) MKSI; LAMBDA1=((TIRE MODF FREQ RANG 1) * 6.28) ** 2; * MKP= KP PP MOD1 FLAM ; MODF=VIBR PROC (PROG 0.) (RIG ET CDL) (MKSI ET MKP); LAMBDA2=((TIRE MODF FREQ RANG 1) * 6.28) ** 2; * SAUT PAGE ; SAUT 5 LIGN ; MESS 'K(SIG) SEUL : ON DOIT TROUVER LAMBDA= 6.66E-6'; MESS ' LE CALCUL DONNE LAMBDA=' LAMBDA1; SAUT 2 LIGN ; * MESS 'K(SIG)+K(P) : ON DOIT TROUVER LAMBDA=5E-6' ; MESS ' LE CALCUL DONNE LAMBDA=' LAMBDA2; SAUT 2 LIGN ; * TEMPS ; *------------- CODE DE FONCTIONNEMENT ---------------- ERR1=100*(ABS(6.66E-6 - LAMBDA1)/6.66E-6); ERR2=100*(ABS(5E-6 - LAMBDA2)/5E-6); ERRMAX=MAXI (PROG ERR1 ERR2); SI (ERRMAX < 5 ); ERRE 0; SINON ; ERRE 5; FINSI; FIN;
Test four1 Comments
TRAC ECLA ELEM CYL; The operator TRAC with keyword ECLA allows to represent the meshing with dispersed elements. Each element is represented with a homothetic rate (0.5 by default). The other keyword ELEM allows to indicate the local number of the elementary objects.
OPTI MODE FOUR NOHARM; The computation mode is defined with the operator OPTI. The keyword NOHARM allows to create objects which coulb be used with any number of harmonic.
OPTI MODE FOUR 0; All objects which are created after this command will be used only with harmonic 0. When the computation is done with harmonic 2, the previous objects are unavailable.
MODF = VIBR PROC (PROG 0.) (RIG ET CDL) MKSI;
LAMBDA1 = ((TIRE MODF FREQ RANG 1) * 6.28) ** 2;
The natural mode shapes are calculated which frequency value is close to zero. The type of
the object MODF is called SOLUTION. MODF has different components among wich the
frequency (component FREQ).
In order to obtain the value of the frequency, we use the operator TIRE with keyword
FREQ to indicate the type of the desired component and the keyword RANG to indicate
the row of the moment. In this case there is only one shape, so the value of the row
is one, but if there were two shapes, the first row would correspond to the lower
frequency and the second to the higher frequency.
PP = MANU CHPO CYL 1 P 1. ;
MKP = KP PP MOD1 FLAM ;
The operator KP creates the pressure matrix joined to the work of pressure in large
displacements. With keyword FLAM, the created object is a mass matrix.