
Test name
dyna6
Calculation type
MECHANICS DYNAMICS 3D
Finite element type
POUT
Topic
Bending mode shape of a clamped-free beam.
The beam is clamped at one end and free on the other end. The problem consists in finding frequencies of the first and second mode shapes of the beam.
The three options of the VIBR operator are tested in this example :

Goal
Find the frequencies of the first and second mode shapes of the beam.
Reference
Analytical solution : Timoshenko.
Version
97' customer version
Model description
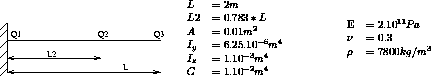
Test dyna6 Results
Results
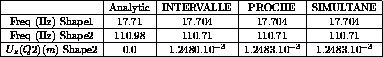
CASTEM figures
* Test Dyna6.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* --------------------------------- *
* *
OPTI ECHO 0;
GRAPH='N';
SAUT PAGE ;
*
*******************************************************
* DYNA6
*
* CAS TEST OPERATEUR VIBRATION
* MODES DE FLEXION D'UNE POUTRE
* ENCASTREE-LIBRE
*
* Cet exemple permet de tester les trois options
* de l'opérateur VIBR :
*
* - par intervalle (INTERVALLE) oº on sépare les
* modes par dichotomie sur un intervalle donné
* - par proximité (PROCHE) oº on recherche les
* modes proches de valeurs données
* - par la méthode de Lanczos (SIMULTANE) oº on
* projette sur un sous-espace
*
*
* Le problème consiste à trouver les fréquences pour
* le premier et le deuxième mode, d'une poutre
* encastrée à une extrémité et libre à l'autre.
*
* Les valeurs obtenues par les trois méthodes sont
* comparées aux valeurs théoriques.
*
*******************************************************
*
TITRE 'FLEXION D UNE POUTRE ENCASTREE-LIBRE';
OPTIO DIME 3 ELEM SEG2 MODE TRID IMPI 0;
TEMPS ;
DENSITE 0.1;
*
*---------------------- MAILLAGE ----------------------
*----------- Q2 EST UN NOEUD POUR LE MODE NUMERO 2 ----
*
Q1 = 0. 0. 0.;Q2 = (2.*0.783) 0. 0. ;Q3 = 2. 0. 0. ;
LIG= Q1 D Q2 D Q3 ;
OEIL1 = 5 5 5 ;
SI(NEG GRAPH 'N');
TRAC OEIL1 LIG ;
FINSI;
*
STAN= MODL LIG MECANIQUE POUT ;
*
*------------ MATERIAU ET CARATERISTIQUES -------------
*
MATPL1=MATR STAN YOUNG 2.E11 NU 0.3 RHO 7800;
CARPL1=CARB STAN SECT 0.01 INRY 6.25E-6 INRZ 1.E-3
TORS 1.E-2;
MATPL1=MATPL1 ET CARPL1;
*
*------------------ RIGIDITE ET MASSE -----------------
*
RIGPL1 =RIGI STAN MATPL1;
MASPLA1=MASS STAN MATPL1 ;
*
*------------------ ON BLOQUE Q1 ----------------------
*
BLOQ1=BLOQ DEPL ROTA Q1 ;
RIGPLA1=RIGPL1 ET BLOQ1 ;
*
*______________________________________________________
* PREMIERE OPTION (INTERVALLE)
* ON SEPARE LES MODES PAR DICHOTOMIE
* PUIS ON LANCE LES ITERATIONS INVERSES
*______________________________________________________
*
MODPLA1=VIBR INTE 10. 120. RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
*
*______________________________________________________
* DEUXIEME OPTION (PROCHE)
* ON LANCE LES ITERATIONS INVERSES
* A PARTIR DES FREQUENCES CONTENUES
* DANS LE LISTREEL
*______________________________________________________
*
PR=PROG 17. 110.;
MODPLA2=VIBR PROC PR RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
*
*______________________________________________________
* TROISIEME OPTION (SIMULTANE)
* ON UTILISE LA METHODE DE LANCZOS
* (PROJECTION SUR UN SOUS-ESPACE)
*______________________________________________________
*
MODPLA3=VIBR SIMU 1. 2 RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
*
*---------------------- R{sultats ---------------------
*
OPTI ECHO 0;
SAUTER PAGE;
F1=TIRE MODPLA1 FREQ RANG 1;
G1=TIRE MODPLA1 FREQ RANG 2;
F2=TIRE MODPLA2 FREQ RANG 1;
G2=TIRE MODPLA2 FREQ RANG 2;
F3=TIRE MODPLA3 FREQ RANG 1;
G3=TIRE MODPLA3 FREQ RANG 2;
*
MESS '*';
MESS '******** ON VERIFIE LES FREQUENCES';
MESS '*';
MESS
' ANALYTIQUE * INTERVALLE * PROCHE
* SIMULTANE';
MESS
' -------------*-----------------*-----------
-----*-------------';
MESS ' MODE 1 17.71 * ' F1 '*' F2 '* ' F3;
MESS ' MODE 2 110.98 * ' G1 '*' G2 '* ' G3;
MESS ' ';
MESS ' ';
MESS '*';
MESS
'******** ON VERIFIE LA DEFORMEE DU DEUXIEME MODE';
MESS '*';
MESS ' ';
X1=EXTR (TIRE MODPLA1 DEPL RANG 2) UZ Q2;
X2=EXTR (TIRE MODPLA2 DEPL RANG 2) UZ Q2;
X3=EXTR (TIRE MODPLA3 DEPL RANG 2) UZ Q2;
MESS
' ANALYTIQUE * INTERVALLE * PROCHE
* SIMULTANE';
MESS
' -------------*-----------------*-----------
-----*-------------';
MESS 'MODE 2 0.00 * ' X1 '*' X2 '* ' X3;
TEMPS ;
* CODE FONCTIONNEMENT
FREF=17.71; GREF=110.98;
RESI1=ABS((F1-FREF)/FREF); RESI2=ABS((G1-GREF)/GREF);
SI((RESI1 <EG 1E-2) ET (RESI2 <EG 1E-2));
ERRE 0;
SINO;
ERRE 5;
FINSI;
FIN;
Test dyna6 Comments
RIGPL1 = RIGI STAN MATPL1;
MASPLA1= MASS STAN MATPL1 ;
The operators RIGI and MASS require the model (here STAN) and the
material and geometrical characteristics (here MATPL1).
The type of these two objects is RIGIDITE. The subtype of RIGPL1 is
RIGIDITE and the subtype of MASPLA1 is MASSE.
MODPLA1 = VIBR INTE 10. 120. RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
The operator VIBR requires the rigidity and mass matrices of the system. VIBR with keyword INTE computes the natural eigen shapes which frequencies are contained between 10 Hz and 120 Hz.
PR = PROG 17. 110.;
MODPLA2 = VIBR PROC PR RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ;
VIBR with keyword PROC computes the natural eigen shapes which frequencies
are the nearest to the given list (here PR).
MODPLA3 = VIBR SIMU 1. 2 RIGPLA1 MASPLA1 ; VIBR with keyword SIMU computes the two natural eigen shapes which frequencies are the nearest to the given real (here 1.).