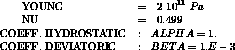
Test name
testICQ4
Calculation type
ISOTROPIC ELASTIC MECHANIC, PLAN DEFO
Finite element type
ICQ4
Topic
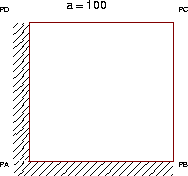
Square plate sujected to hydrostatic and deviatoric loads.
A square plate is embedded at two adjacent sides. Deviatoric
and hydrostatic loads are applied to each side.
Goal
Test the ICQ4-incompressible elements.
Reference CASTEM
Rapport DMT sur les elements ICQ4.
Version
97' customer release
Model description
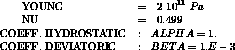
* Test TestICQ4.dgibi: Jeux de données *
* ------------------------------------ *
* *
*
* FICHIER GIBIANE POUR TESTER LES ELEMENTS
* INCOMPRESSIBLES ICQ4
*
* Maillage d'une plaque de forme carrée avec les
* éléments ICQ4.
*
* Cas déformation plane.
*
* On soumet la plaque à un champ de contrainte
* hydrostatique (contribution: alpha=1) et à un champ
* de contrainte déviatorique (contribution: beta=0.001)
*
* Les résultats théoriques sont déterminés dans le cas
* incompressible (coefficient de Poisson proche de 0.5)
*
* cf rapport DMT sur ces elements
*
*
*-----MAILLAGE-----------
*
opti dime 2 mode plan defo elem qua4 ;
*
p1 = 0. 0. ;
p2 = 100. 0. ;
p3 = 100. 100. ;
p4 = 0. 100. ;
*
li1 = d 10 p1 p2 ;
li2 = d 10 p2 p3 ;
li3 = d 10 p3 p4 ;
li4 = d 10 p4 p1 ;
*
sur1 = dall li1 li2 li3 li4 'PLAN' ;
*
*
*-----MODELE MECANIQUE------------
*
* Valeur du coefficient de Poisson
*
nu1 = 0.499 ;
*
mod1 = modele sur1 'MECANIQUE' 'ELASTIQUE' 'ISOTROPE'
icq4 ;
mat1 = mate mod1 'YOUNG' 2.e11 'NU' nu1 ;
rigi1 = rigi mod1 mat1 ;
*
*
*-----CONDITIONS AUX LIMITES------------
*
bl1 = bloq li1 'UY' ;
bl2 = bloq li4 'UY' ;
bl3 = bloq p1 'UX' ;
*
*
*----------------CHARGEMENT-----------------
*
* Coefficients de contribution de chargement
* (alpha-->hydrostatique)
* (beta-->déviatorique)
*
alpha = 1. ;
beta = 1.e-3 ;
*
*-----Chargement déviatorique------------
*
*-----sur li1-----
*
chpx1 = coor 1 li1 ;
chpresy1 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (chpx1 * (-2.)*1.e5) ;
chpres1 = beta * chpresy1 ;
vecfor1 = vect chpres1 1.E-7 'FX' 'FY' rouge ;
*
*-----sur li2-----
*
chpy2 = coor 2 li2 ;
chpresx2 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (200.*1.e5) li2 ;
chpresy2 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (chpy2 * (-2.)*1.e5) ;
chforx2 = chpresx2 ;
chfory2 = exco 'FX' chpresy2 'FY';
chpres2 = beta * ( chforx2 et chfory2 ) ;
vecfor2 = vect chpres2 'FX' 'FY' 1.E-7 rouge ;
*
*-----sur li3-----
*
chpx3 = coor 1 li3 ;
chpresx3 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (-200.*1.e5) li3 ;
chpresy3 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (chpx3 * (-2.)*1.e5) ;
chforx3 = exco 'FY' chpresx3 'FX';
chfory3 = chpresy3 ;
chpres3 = beta * ( chforx3 et chfory3 ) ;
vecfor3 = vect chpres3 'FX' 'FY' 1.E-7 rouge ;
*
*-----sur li4-------
*
chpy4 = coor 2 li4 ;
chpresy4 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (chpy4 * (-2.)*1.e5) ;
chfory4 = exco 'FX' chpresy4 'FY';
chpres4 = beta * chfory4 ;
vecfor4 = vect chpres4 1.E-7 'FX' 'FY' rouge ;
*
*
*-----Chargement hydrostatique------------
*
*-----sur li1-----
*
presy1 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (1.e5) li1 ;
pres1 = alpha * presy1 ;
vfor1 = vect pres1 1.E-5 'FX' 'FY' vert ;
*
*-----sur li2-----
*
presx2 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (1.e5) li2 ;
pres2 = alpha * presx2 ;
vfor2 = vect pres2 'FX' 'FY' 1.E-5 vert ;
*
*-----sur li3-----
*
presy3 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (1.e5) li3 ;
pres3 = alpha * presy3 ;
vfor3 = vect pres3 'FX' 'FY' 1.E-5 vert ;
*
*-----sur li4-------
*
presx4 = pres 'MASS' mod1 (1.e5) li4 ;
pres4 = alpha * presx4 ;
vfor4 = vect pres4 1.E-5 'FX' 'FY' vert ;
*
*
*---------CALCUL DES DEPLACEMENTS --------------------
*
*
* Solution analytique au point P3: uyan.
*
x3 = coor 1 p3 ;
y3 = coor 2 p3 ;
mu = 1.e11 / ( 1 + nu1 ) ;
uyan = ( 2 * x3 * y3 ) / ( 2 * mu ) * 1.e5 * beta ;
*
* Solution Castem au point P3: uycas.
*
deptot = reso (rigi1 et bl1 et bl2 et bl3)
(chpres2 et chpres3 et chpres4 et chpres1
et pres2 et pres3 et pres4 et pres1) ;
uycas = extr deptot 'UY' p3 ;
*
* Calcul de l'erreur sur le déplacement.
*
erry = abs (( uyan - uycas ) / ( uyan )) * 100 ;
*
* Test de précision sur le calcul du déplacement uy
* (<1%).
*
si ( erry >eg 1. ) ;
erreur 5 ;
finsi ;
*
*
*-----------CALCUL CONTRAINTES-------------------------
*
*
* Solution analytique: pression = alpha*1.E5.
*
* Solution Castem : pression maximale = maxpres1.
*
sig1 = sigma mod1 deptot mat1 ;
sxx = exco 'SMXX' sig1 'P' ;
syy = exco 'SMYY' sig1 'P' ;
szz = exco 'SMZZ' sig1 'P' ;
sp = (sxx + syy + szz) / 3. ;
maxpres1 = maxi sp ;
*
* Calcul de l'erreur sur la pression.
*
errpress = abs ((maxpres1 + (alpha * 1.E5)) /
(alpha * 1.E5)) * 100. ;
*
* Test de précision sur le calcul de la pression (<1%).
*
si ( errpress >eg 1. ) ;
erreur 5 ;
finsi ;
*
*
fin;
Test testICQ4 Comments
OPTI DIME 2 MODE PLAN DEFO ELEM QUA4 ; MOD1 = MODE SUR1 MECANIQUE ELASTIQUE ISOTROPE ICQ4 ;The incompressible quadrangle with four nodes ICQ4 is a finite element of the QUA4 geometrical support in MECANIQUE.
BETA = 1.E-3 ; *-----ON LI1----- CHPX1 = COOR 1 LI1 ; CHPRESY1 = PRES MASS MOD1 (CHPX1 * (-2.)*1.E5) ; CHPRES1 = BETA * CHPRESY1 ; VECFOR1 = VECT CHPRES1 1.E-7 FX FY ROUG ;The COOR operator enables the user to recover the Nith coordinate (here the first, then UX) of the MAILLAGE (LT1) type object.
The PRES operator calculates the nodal forces which are equivalent
to a pressure applied on an object. Here this operator is connected
by key words MASS reffering to the type of element on which is applied.
MOD1 is the object on which the pressure is appiled (MMODEL type).
The pressure (FLOTTANT type) (-2)*1.E-5 is negative because
it is carried by the negative normal to the element.
The VECT operator constructs a VECTEUR type object (VECTFOR1)
from the components of a vector field (CHPRES1), and 1.E-7 is
the coefficient of amplification (FLOTTANT type). The names
of the components of the field associated with the directions
Ox, Oy (MOT type) are FX and FY.
ALPHA = 1. PRESX2 = PRES MASS MOD1 (1.E5) LI2 ; PRES2 = ALPHA * PRESX2 ; VFOR2 = VECT PRES2 FX FY 1.E-5 VERT ;